- WeAreHuman@Work
- Posts
- WeAreHuman - Issue 003
WeAreHuman - Issue 003
WeAreHuman is a newsletter dedicated to fostering a more sustainable world of work.

THIS WEEK'S CONTENT
If you just want links and a brief description of the topics covered, you will find the information at a glance below. If you prefer a deeper dive, scroll down to the rest of the newsletter.
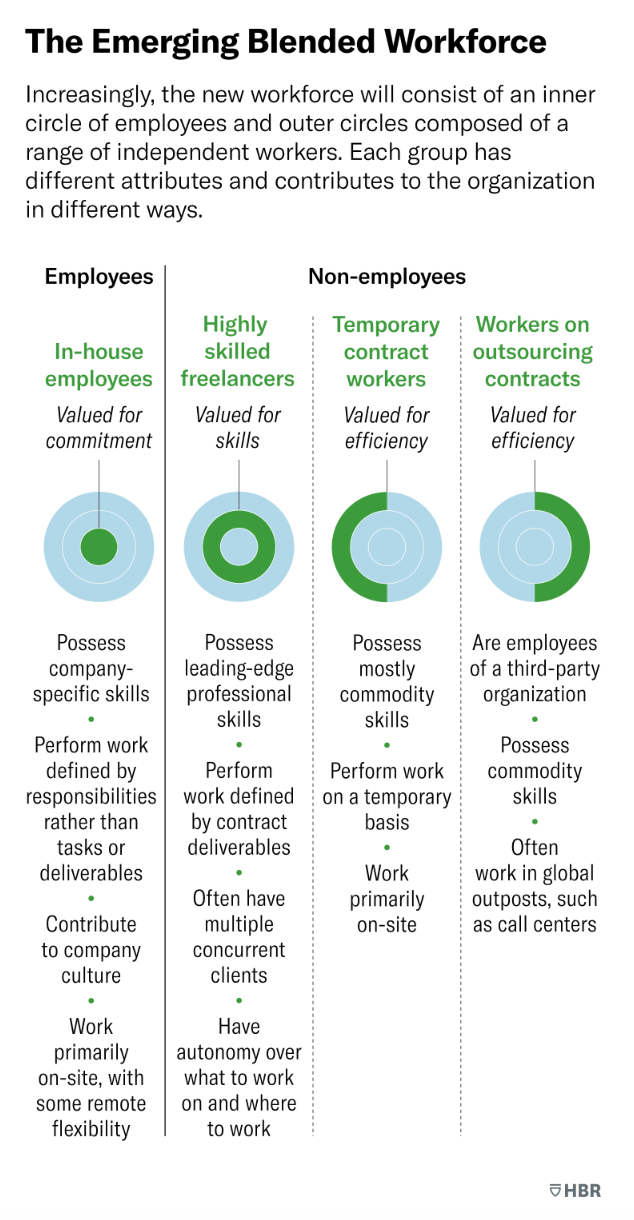
GLOBAL WORKFORCE MANAGEMENT | Harvard Business Review | Highly Skilled Professionals Want Your Work But Not Your Job
This article explores the growing trend of highly skilled professionals preferring freelance work over full-time employment and how companies can effectively manage a blended workforce of employees and freelancers to meet their talent needs.
EMPLOYABILITY & LEARNING CULTURE | MIT Sloan Management Review | Why You Should Let Your Favorite Employee Move to Another Team
This article explores the detrimental effects of internal talent hoarding and highlights the benefits managers can gain by supporting their employees' career advancement.
DIVERSITY, EQUITY & INCLUSION | McKinsey & Company | Women in the Workplace 2024: The 10th-anniversary report
This comprehensive study, conducted in partnership with LeanIn, marks a decade of tracking women's experiences in corporate America. It highlights progress, ongoing challenges, and recommendations for fostering gender equity in the workplace.
HYBRID WORKING | Nature | Hybrid Working from Home Improves Retention Without Damaging Performance
This study demonstrates that hybrid work boosts employee retention and satisfaction while maintaining performance levels, countering executive concerns about the productivity of remote work.
GLOBAL WORKFORCE MANAGEMENT | Harvard Business Review | Highly Skilled Professionals Want Your Work But Not Your Job
This article explores the growing trend of highly skilled professionals preferring freelance work over full-time employment and how companies can effectively manage a blended workforce of employees and freelancers to meet their talent needs.
DID YOU KNOW?
“Over one-third of companies (35%) now rely on freelancers for strategic, high-impact work, reflecting a significant shift in workforce dynamics.”
DID YOU SEE?
NEED AN EXECUTIVE SUMMARY?
Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, companies face a significant talent management challenge as they strive to transform their offerings, processes, and infrastructures. This article explores the growing trend of highly skilled professionals opting for freelance work over traditional full-time employment and the implications for organisations seeking to harness top talent.
Key Insights
Talent Shortage: Many companies lack essential in-house capabilities for digital transformation and cannot persuade top talent to join full-time despite attractive offers.
Freelance Preference: The most sought-after professionals in technology, data sciences, and machine learning increasingly choose to work as freelancers.
Perceived Opportunities: 65% of knowledge workers believe they can find better freelancer opportunities than full-time employees.
Executive Expectations: Due to talent shortages, 73% of executives anticipate relying more on freelancers in the coming years.
Managerial Challenge: Managing a "blended workforce" of full-time employees and highly skilled freelancers is becoming a critical managerial challenge.
Inadequate Models: Traditional temporary staffing models are inadequate for integrating skilled freelancers effectively into cohesive internal teams.
Drivers of Freelance Work: The rise of freelance work is driven by factors such as the desire for flexibility, diverse project experiences, and the ability to command higher rates.
Recommendations
Develop a comprehensive blended workforce strategy: Create a holistic plan for integrating freelancers into your organisation, addressing issues such as team dynamics, communication, project management, and knowledge transfer.
Redesign onboarding and integration processes: Tailor onboarding procedures specifically for highly skilled freelancers to ensure they quickly understand company culture, processes, and project goals.
Implement collaborative technologies: Invest in digital platforms facilitating seamless collaboration between in-house staff and external professionals. Ensure that freelancers have appropriate access to necessary systems and information while maintaining data security.
Adapt management practices: Train managers to lead and motivate blended teams effectively, focusing on output and results rather than traditional employment metrics. Develop new performance evaluation methods that account for the contributions of full-time employees and freelancers.
Review and update policies: Examine existing HR policies and procedures to ensure they accommodate the unique needs of a blended workforce while maintaining compliance with labour regulations. This may include revising contracts, intellectual property agreements, and confidentiality clauses.
Foster a culture of integration: Encourage full-time employees to view freelancers as valuable team members, promoting knowledge sharing and collaborative problem-solving. Organise team-building activities that include both permanent staff and freelancers to build cohesion and trust.
Establish clear communication channels: Create structured communication protocols to inform freelancers of project updates, organisational changes, and other relevant information. Regular check-ins and feedback sessions can help maintain alignment and address any issues promptly.
Develop a talent pipeline: Build relationships with high-quality freelancers and consider creating a talent pool for future projects. This can help streamline finding and onboarding skilled professionals when needs arise.
Conclusion
The emergence of the blended workforce presents both challenges and opportunities for organisations. By embracing this new reality and implementing strategies to integrate highly skilled freelancers effectively, companies can access top talent, enhance their capabilities, and drive innovation. Success in this new landscape will depend on adaptability, effective management practices, and a willingness to rethink traditional employment models.
WANT THE COMPLETE STORY?
Access the source here.
EMPLOYABILITY & LEARNING CULTURE | MIT Sloan Management Review | Why You Should Let Your Favourite Employee Move to Another Team
This article explores the detrimental effects of internal talent hoarding and highlights the benefits managers can gain by supporting their employees' career advancement.
DID YOU KNOW?
“75% of managers engage in talent hoarding, intentionally keeping skilled employees in their current roles despite growth opportunities elsewhere.”
NEED AN EXECUTIVE SUMMARY?
Introduction
In today's dynamic business environment, managers often face the dilemma of supporting their career advancement or retaining them within their teams. This article explores the concept of internal talent hoarding and its implications for both managers and organisations.
Key Insights
Prevalence of Talent Hoarding: 75% of managers admit to hoarding talent, with the actual percentage likely higher due to social desirability bias.
Career Advancement Barriers: Many companies require employees to get their current manager's approval to apply internally, enabling managers to block promotions directly.
Attraction of Top Talent: Managers with higher rates of promoting subordinates received 43% more internal applications overall and 66% more applications from employees rated as high performers.
Functional Diversity: Managers supporting employee advancement attracted 32% more applicants from other functions than those with lower promotion rates.
Reputation Effects: A manager's reputation for supporting promotions follows them throughout the organisation, even when changing roles.
Long-Term Impact: Managers who promoted employees at higher rates continued to receive more applications in subsequent years, with the effect persisting for at least three years.
Recommendations
Implement robust internal talent markets: Create transparent systems for employees to view and apply for internal opportunities. Encourage managers to post all job openings internally and consider implementing an internal talent marketplace platform.
Incentivise talent development: Establish financial rewards for managers who successfully promote subordinates, similar to Chipotle's $10,000 bonus for general managers who train crew members to become managers.
Enhance leadership performance metrics: Incorporate measures of a manager's ability to develop and advance team members into leadership ratings. Include metrics such as promotion rates and diversity of internal applicants.
Foster a culture of internal mobility: Encourage open discussions about career growth and normalise cross-team moves. Train managers to have regular career conversations with team members and support their development.
Track and analyse promotion rates: Use HR systems to monitor managers' success in advancing employees. Share best practices from high-performing managers and identify areas where talent hoarding may occur.
Address misconceptions about talent mobility: Educate managers on the long-term benefits of supporting employee advancement, such as attracting higher-quality applicants and fostering innovation.
Conclusion
Managers can become talent magnets by supporting internal talent mobility, attracting high-quality applicants and fostering innovation within their teams. Organisations that discourage talent hoarding and promote internal advancement will likely see improved retention rates, reduced recruiting costs, and a more engaged, productive workforce.
WANT THE COMPLETE STORY?
Access the source here.
DIVERSITY, EQUITY & INCLUSION | McKinsey & Company | Women in the Workplace 2024: The 10th-anniversary report
This comprehensive study, conducted in partnership with LeanIn, marks a decade of tracking women's experiences in corporate America. It highlights progress, ongoing challenges, and recommendations for fostering gender equity in the workplace.
DID YOU KNOW?
“For the first time in 10 years, companies are reporting a decline in career development, mentorship, and sponsorship programs for women, as well as in recruitment and internship initiatives specifically focused on advancing female talent.”
DID YOU SEE?

NEED AN EXECUTIVE SUMMARY?
Introduction
The Women in the Workplace 2024 report, published by McKinsey & LeanIn.Org, marks a decade of tracking women's progress in corporate America. It presents actionable insights for leaders, highlighting advancements and persistent challenges related to gender diversity, inclusion, and workplace equity.
Key Insights
C-suite Representation: Women now hold 29% of C-suite roles, up from 17% in 2015, showing steady progress. However, women of colour remain underrepresented at 7% of C-suite positions.
The "Broken Rung": For every 100 men promoted to manager, only 81 women achieve the same level, dropping to 54 Black women for every 100 men. This bottleneck significantly hinders the leadership pipeline for women.
Persistent Bias: 42% of senior women have witnessed microaggressions against other women, compared to just 10% of senior men, demonstrating ongoing issues in workplace culture. Additionally, women of colour, LGBTQ+ women, and women with disabilities face the highest rates of demeaning interactions.
Work-Life Balance: Around 40% of women say they are responsible for most household work, the same percentage reported in 2016, while more men believe household duties are equally shared.
Recommendations
Strengthen Career Support: Equip managers with tools and resources to actively support women’s career growth and advancement, ensuring they provide guidance and feedback tailored to women’s unique challenges.
Address Micro-aggressions: Implement stricter accountability measures and comprehensive training to reduce micro-aggressions and make the workplace more inclusive and supportive of women.
Enhance Allyship Programs: Revise bias and allyship training to ensure it leads to tangible, measurable behaviour changes, fostering a more collaborative environment for women, particularly those from marginalised groups.
Prioritise Work-Life Balance: Encourage policies that support flexible work arrangements, particularly for women managing caregiving responsibilities, to reduce the work-life disparity they face.
Conclusion
The findings from this report highlight the importance of focused and sustained efforts to overcome deeply ingrained biases and barriers for women in corporate America. By implementing these strategies, organisations can create a more inclusive environment and promote the advancement of women at all levels, driving meaningful progress in gender parity and workplace equity.
WANT THE COMPLETE STORY?
Access the source here.
HYBRID WORKING | Nature | Hybrid Working from Home Improves Retention Without Damaging Performance
This study demonstrates that hybrid work boosts employee retention and satisfaction while maintaining performance levels, countering executive concerns about the productivity of remote work.
DID YOU KNOW?
“Remote work reduced employee turnover by 33% overall, with especially significant impacts on non-managerial staff, women, and employees facing longer commutes”.
DID YOU SEE?

NEED AN EXECUTIVE SUMMARY?
Introduction
A groundbreaking study published in Nature explores the impact of hybrid working arrangements on employee retention, job satisfaction, and performance. This six-month randomised control trial, conducted at a Chinese technology company, provides valuable insights into the effects of hybrid work schedules on various aspects of employee and organisational outcomes.
Key Insights
Hybrid working improves retention and job satisfaction
The study found that hybrid working reduced quit rates by one-third.
Job satisfaction scores improved among employees with hybrid schedules.
Performance remains unaffected
Null equivalence tests showed no significant impact on performance grades over the next two years of reviews.
No evidence was found for differences in promotion rates over the next two years.
Demographic variations in benefits
The reduction in quit rates was particularly significant for non-managers, female employees, and those with long commutes.
Productivity perceptions shift
Managers revised their views on hybrid working's effect on productivity from an initial perceived negative impact of -2.6% to a positive +1.0% after the experiment.
Recommendations
Implement hybrid work options
Consider offering employees the option to work from home twice weekly to improve retention and job satisfaction.
Address demographic differences
When designing policies, pay special attention to the benefits of hybrid work for non-managers, women, and employees with long commutes.
Monitor performance metrics
Regularly assess performance and promotion rates to ensure hybrid arrangements do not negatively impact these areas.
Educate managers
Provide training and information to managers about the potential benefits of hybrid work to address initial scepticism.
Conclusion
This study proves that a hybrid schedule with two days of working from home per week can significantly improve employee retention and satisfaction without compromising performance. Organisations considering or refining their hybrid work policies can use these findings to inform their decisions and potentially reap the benefits of increased employee retention and satisfaction.
WANT THE COMPLETE STORY?
Access the source here.