- WeAreHuman@Work
- Posts
- WeAreHuman - Issue 004
WeAreHuman - Issue 004
WeAreHuman is a newsletter dedicated to fostering a more sustainable world of work.

THIS WEEK'S CONTENT
If you just want links and a brief description of the topics covered, you will find the information at a glance below. If you prefer a deeper dive, scroll down to the rest of the newsletter.
PEOPLE SUSTAINABILITY STRATEGY | Gartner | The Human-Powered Enterprise: How Human Resources Fuel Superior Organizational Performance | This report highlights the critical role of a human-powered enterprise, emphasising the importance of integrating human-centric leadership, diversity, employee well-being, and a human-AI partnership to drive superior organisational performance and foster a more engaged and resilient workforce.
HYBRID WORKING | The Talent Strategy Group | Above the Fray: What We Know About How WFH and Hybrid Affect Work | This article examines the effects of working from home (WFH) and hybrid work on performance, innovation, and collaboration. It dispels myths surrounding WFH and provides evidence-based insights for HR leaders, highlighting benefits and challenges while emphasising the importance of understanding how work arrangements impact organisational outcomes.
HEALTH, WELL-BEING, & PSYCHOLOGICAL SAFETY | Boston Consulting Group | Facing Deskless Labor Shortage with Technology | This article discusses how companies can address deskless labour shortages by using technology to improve communication, reduce physical strain, and boost engagement. By integrating digital tools, organisations can enhance the working conditions of deskless workers, leading to better retention, higher job satisfaction, and improved productivity.
PAY EQUITY & TRANSPARENCY | Dayforce | 2024 Dayforce Living Wage Index | The 2024 Living Wage Index, published by Dayforce, explores wage disparities in the U.S. workforce. It reveals that 44% of full-time workers do not earn enough to cover basic needs. Women, Black, and Latino workers are disproportionately affected, and specific industries like leisure, hospitality, and retail face significant wage challenges.
PEOPLE SUSTAINABILITY STRATEGY
Gartner | The Human-Powered Enterprise: How Human Resources Fuel Superior Organizational Performance | This report highlights the critical role of a human-powered enterprise, emphasising the importance of integrating human-centric leadership, diversity, employee well-being, and a human-AI partnership to drive superior organisational performance and foster a more engaged and resilient workforce.
DID YOU KNOW?
“Companies that integrate diversity with a strong sense of belonging achieve significantly higher employee engagement and performance. It's not just about diversity numbers, but about how included and connected their people feel.”
DID YOU SEE?

6 Key Features of The Human-Powered Enterprise
NEED AN EXECUTIVE SUMMARY?
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic catalysed a shift towards a more empathetic, human-centric approach to people management. This human-powered enterprise model focuses on treating employees as people, not just workers, to maximise their performance and drive superior business outcomes. With the pandemic’s direct impact behind us, maintaining a human-centred workplace is crucial for future success.
Key Insights - Six Key Features of Human-Powered Enterprises
Feature #1: Why We Work – A Human Deal
Modern EVPs should focus on life experiences and emotions, not just job features. Organisations can boost retention, engagement, and overall performance by making employees feel valued, autonomous, and understood. Recognising the full spectrum of employee needs is critical to this approach.
Feature #2: How We Work – A Strategy for Workforce Well-Being
Rather than treating well-being as an add-on, companies need to embed it into everyday work processes. Incorporating proactive rest, flexibility, and autonomy into work reduces fatigue and frustration and increases productivity across the workforce.
Feature #3: Who We Work With – Integration of Diversity and Belonging
Organisations that combine diversity with a strong sense of belonging achieve higher engagement and performance. DEI initiatives should be integrated into business processes, ensuring diversity and belonging are central to the organisation's operations.
Feature #4: Who We Work For – A New Call for Human Leadership
Leaders must focus on demonstrating authenticity, empathy, and adaptability. Rather than just building skills, leaders should overcome emotional barriers to connect with their teams and lead more effectively.
Feature #5: Where We Work – The Human-Centric Workplace
Workplaces should provide autonomy, capability, and connection, whether employees work on-site, remotely, or in a hybrid model. Organisations foster higher levels of productivity and engagement by creating conditions where employees can perform at their best.
Feature #6: What Supports Our Work – A Human-AI Partnership
In a human-powered enterprise, AI should enhance human potential by creating opportunities for people to maximise their creativity and innovation. Organisations should focus on building partnerships between AI and human workers for long-term success.
Recommendations
Redesign Employee Value Propositions (EVPs): Focus on life experiences and emotions rather than work features. EVPs should make employees feel understood, autonomous, and valued, improving retention, engagement, and performance.
Embed Well-Being into Work: Instead of offering well-being as a separate benefit, organisations should integrate proactive rest, flexibility, and autonomy into daily workflows. This will reduce fatigue and frustration, fostering sustainable high performance.
Integrate Diversity and Belonging into Business Processes: DEI should not be an isolated initiative. Organisations must combine diversity with a strong sense of belonging, making it a core element of business operations. This leads to higher engagement and performance.
Develop Human Leadership: Leaders should focus on authenticity, empathy, and adaptability, overcoming emotional barriers rather than simply enhancing technical leadership skills. Human leadership helps connect more deeply with employees and improves well-being and engagement.
Create a Human-Centric Workplace: Ensure that the workplace — on-site, remote, or hybrid — provides employees with autonomy, capability, and connection. This creates an environment where employees can perform at their best.
Build a Human-AI Partnership: HR leaders should encourage a collaborative approach in which AI enhances human potential rather than replaces it. Organisations can drive creativity, innovation, and future growth by fostering a partnership between AI and human workers.
Conclusion
The human-powered enterprise model is essential for organisations looking to thrive in a post-pandemic world. Organisations can drive employee engagement and superior business outcomes by embedding well-being, integrating diversity, fostering human leadership, and promoting AI-human collaboration. Reverting to traditional models risks missing out on these significant advantages.
HYBRID WORKING
The Talent Strategy Group | Above the Fray: What We Know About How WFH and Hybrid Affect Work | This article examines the effects of working from home (WFH) and hybrid work on performance, innovation, and collaboration. It dispels myths surrounding WFH and provides evidence-based insights for HR leaders, highlighting benefits and challenges while emphasising the importance of understanding how work arrangements impact organisational outcomes.
DID YOU KNOW?
“Employees who preferred office work exhibited up to 27% lower productivity when required to work remotely.”
NEED AN EXECUTIVE SUMMARY?
Introduction
This report provides a fact-based analysis of how Work-From-Home (WFH) and hybrid work models impact employee performance, innovation, collaboration, and relationships. As the shift to remote work continues post-pandemic, HR leaders must understand the trade-offs based on emerging research.
Key Insights
Performance Declines in WFH: Studies show that WFH can negatively impact productivity. In a study of Indian data entry workers, those working from home experienced an 18% decline in productivity, and employees who preferred office work showed up to 27% lower productivity when forced to work remotely. Another study from an Indian technology company noted productivity drops of 8% to 19% in WFH settings. These findings highlight that remote work, while feasible, often results in lower individual output.
Challenges in Creativity and Innovation: Remote work has been linked to reduced creativity. Videoconferencing, a vital tool in remote work, narrows cognitive focus and hampers idea generation. Research further indicates that while the quantity of ideas during remote work may not decline significantly, the quality of innovation suffers. Hybrid teams with inconsistent in-office schedules reported less coordination and lower innovation outcomes.
Weakened Work Relationships and Collaboration: WFH environments tend to erode professional relationships. A study of Microsoft employees showed reduced "weak-tie" relationships, essential for cross-department collaboration and flexibility. Employees in remote settings focus more on established connections, reducing the breadth of their professional networks. Another study indicated that remote work polarised perceptions of colleagues, reinforcing biases formed during limited in-person interactions.
Bias Against Remote Workers: WFH employees face potential biases in promotion and advancement opportunities. A UK study found that remote workers, particularly men and childless women, are less likely to receive promotions or salary increases compared to their office-based peers. This suggests that proximity to management plays a role in career progression, even when the work setting does not affect performance.
Recommendations
Tailor Productivity Solutions: For companies experiencing productivity drops in WFH settings, consider structured hybrid models where employees split their time between home and office. This approach can help balance flexibility with the benefits of in-person collaboration.
Enhance Remote Collaboration Tools: Invest in advanced tools and practices that foster creativity and innovation in remote settings. Encouraging brainstorming sessions and virtual team-building activities can help mitigate the cognitive limitations of videoconferencing.
Support Relationship-Building: Encourage remote workers to actively engage in networking activities, both formal and informal. Scheduling regular virtual check-ins and fostering cross-team collaborations can help maintain the "weak-tie" connections crucial for organisational flexibility.
Address Bias in Career Development: Establish clear, objective criteria for promotions and career advancement independent of work location. Regularly train managers to reduce proximity bias and ensure remote employees receive equal growth opportunities.
Conclusion
While WFH and hybrid models offer flexibility, the emerging data reveals challenges in productivity, innovation, and work relationship. By addressing these issues proactively, HR leaders can create a more effective and inclusive workplace that maximises remote and in-office work benefits.
HEALTH, WELL-BEING & PSYCHOLOGICAL SAFETY
Boston Consulting Group | Facing Deskless Labor Shortage with Technology | This article discusses how companies can address deskless labour shortages by using technology to improve communication, reduce physical strain, and boost engagement. By integrating digital tools, organisations can enhance the working conditions of deskless workers, leading to better retention, higher job satisfaction, and improved productivity.
DID YOU KNOW?
“Deskless employees, who make up 70%-80% of the global workforce, face challenges like physical demands and limited communication. As a result, 53% feel burned out, and 43% are looking for new jobs”.
DID YOU SEE?
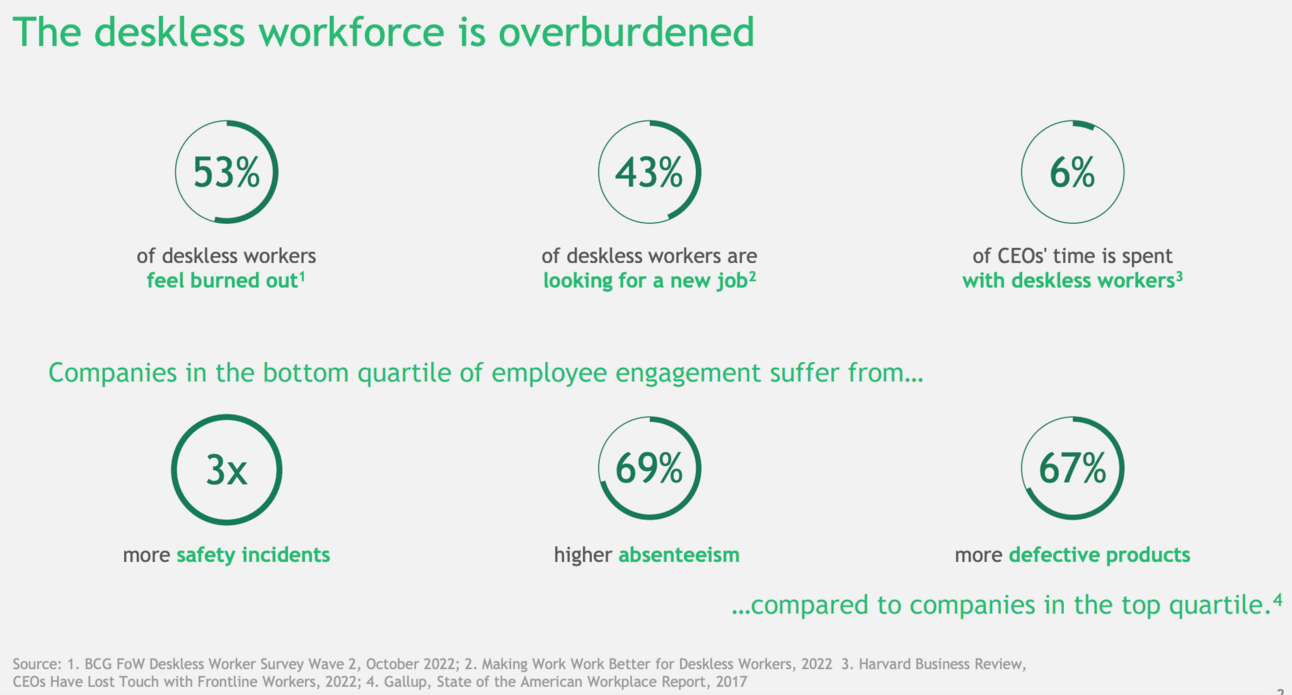
Figure: The Deskless Workforce is Overburden
NEED AN EXECUTIVE SUMMARY?
Introduction
The report by Boston Consulting Group addresses the global deskless labour shortage and the pressing need for technological solutions to enhance deskless workers' experiences. Deskless employees, who make up 70%-80% of the global workforce, face distinct challenges due to their reliance on physical presence, limited communication channels, and the demanding nature of their roles. Technology can play a pivotal role in mitigating these challenges and improving job satisfaction, retention, and productivity.
Key Insights
Employee Burnout and Turnover: Deskless workers are experiencing high levels of burnout, with 53% reporting fatigue and 43% actively seeking new jobs. This turnover is costly, as replacing workers can cost up to 10% of their annual salary. Companies with low employee satisfaction see 33% higher turnover and 15% lower productivity.
Technology Gaps: Many deskless workers are digitally disconnected, with 66% lacking access to corporate mobile devices. Despite advancements in consumer technology, enterprise systems often need to provide deskless employees with the user-friendly tools they need, negatively impacting their productivity and engagement.
Employee Engagement and Retention: Companies focusing on the emotional and functional needs of deskless workers see significant improvements in engagement. Addressing factors such as feeling respected and valued correlates with a 3.2x increase in motivation and a 72% reduction in attrition. Effective use of technology also leads to a 30% decrease in job-seeking behaviour and a 46% drop in stress.
Business Impact of Employee Experience: Optimising deskless employee experiences translates directly into business benefits, including enhanced collaboration, real-time problem-solving, and improved operational efficiency. Companies leveraging digital tools for communication and task management are able to reduce absenteeism by 41% and improve overall performance.
Recommendations
Invest in Digital Tools for Deskless Employees: Provide deskless workers with easy-to-use, mobile-friendly tools that integrate with existing enterprise systems. This could reduce inefficiencies like manual paperwork and improve real-time communication, enabling workers to manage shifts, access training, and stay informed.
Focus on Employee Engagement: Engage deskless workers by addressing their specific needs, such as offering a platform for feedback, recognising their contributions, and improving access to personal development opportunities. These initiatives can lead to a 13.9x improvement in engagement and significantly lower attrition rates.
Streamline Communication: Implement digital platforms for seamless communication between management and deskless employees. This ensures that critical updates and corporate messages are consistently delivered, reducing operational errors and improving employee connection with the company’s goals.
Equalize the Digital Experience: Ensure that deskless workers receive the same level of digital support as their desk-bound counterparts. By closing this gap, businesses can foster inclusivity, improve workforce morale, and enable smoother department operations.
Conclusion
Addressing the unique challenges of deskless workers through technological investment is critical for organisations facing labour shortages. By improving engagement, streamlining communication, and providing accessible digital tools, companies can enhance retention, reduce burnout, and ultimately drive operational excellence. For HR leaders, the focus must shift from reactive recruitment to proactive retention, ensuring that deskless employees are empowered to succeed in today’s demanding work environments.
PAY EQUITY & TRANSPARENCY
Dayforce | 2024 Dayforce Living Wage Index | The 2024 Living Wage Index, published by Dayforce, explores wage disparities in the U.S. workforce. It reveals that 44% of full-time workers do not earn enough to cover basic needs. Women, Black, and Latino workers are disproportionately affected, and specific industries like leisure, hospitality, and retail face significant wage challenges.
DID YOU KNOW?
“Deskless employees, who make up 70%-80% of the global workforce, face challenges like physical demands and limited communication. As a result, 53% feel burned out, and 43% are looking for new jobs”.
DID YOU SEE?
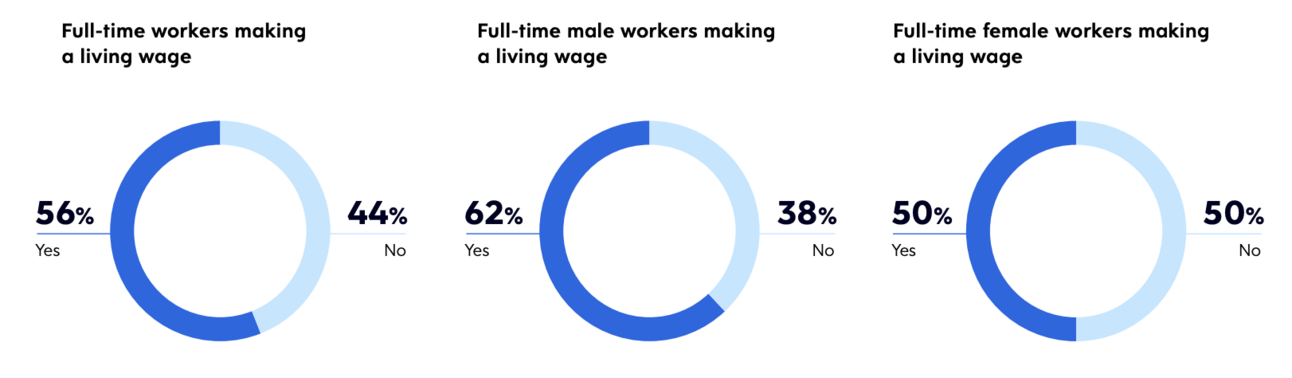
Figure: 2024 Dayforce Living Wage Index
NEED AN EXECUTIVE SUMMARY?
Introduction
The 2024 Dayforce Living Wage Index reveals the widespread issue of full-time workers in the U.S. struggling to meet basic needs, with only 56% earning a living wage. The report highlights income disparities across gender, race, geography, and industry, providing critical insights into the state of wages in the American workforce.
Key Insights
Living Wage Shortfall: Despite being one of the wealthiest nations, 44% of full-time workers in the U.S. do not earn enough to cover basic living expenses, based on a family model with two working adults and two children.
Gender Disparity: Women are disproportionately affected, being 32% more likely than men to earn below a living wage. On average, women earn $4.20 less per hour than men.
Racial and Ethnic Gaps: Only 40% of Black and Latino workers earn a living wage, making them nearly twice as likely as white workers to fall below this threshold. Black and Latino workers earn $8.20 and $7.70 less per hour, respectively, compared to white workers.
Geographic Variations: In major cities like Miami, Phoenix, Los Angeles, and New York, more than 40% of full-time workers do not earn a living wage. The problem is more pronounced in some metropolitan regions, with up to 63% of Washington, D.C. and Houston workers earning above the living wage.
Industry-Specific Challenges: Low-wage jobs are concentrated in specific sectors. Nearly 70% of leisure and hospitality workers, 64% of retail workers, and more than half of healthcare workers do not earn enough to meet basic needs.
Recommendations
Adopt Living Wage Policies: Employers should reassess their wage structures to ensure workers are compensated fairly. Introducing a living wage policy could significantly improve employee well-being and reduce turnover, especially in hospitality, retail, and healthcare industries where wage shortfalls are most severe.
Address Gender Pay Gaps: Organisations must actively monitor and rectify gender-based wage discrepancies. Implementing transparent pay scales and promoting equitable advancement opportunities could help bridge the gender wage gap.
Support Minority Workers: To mitigate racial inequality, targeted efforts like wage adjustments and professional development programs should be introduced. Providing mentorship and career growth pathways for underrepresented groups can foster long-term wage equity.
Tailored Solutions for High-Cost Areas: Companies operating in high-cost cities should consider cost-of-living salary adjustments. Localised wage benchmarks can ensure workers in expensive metropolitan areas earn enough to cover living expenses.
Industry-Specific Strategies: Employers in industries with low wages, such as hospitality and retail, should explore wage enhancements coupled with benefits like flexible scheduling and healthcare support to attract and retain talent. Investment in employee training and career progression can also enhance job satisfaction and earnings potential.
Conclusion
The 2024 Living Wage Index starkly reminds us of the wage disparities affecting nearly half of the U.S. workforce. By addressing these gaps, employers can foster healthier, more productive workplaces, ensuring their employees survive and thrive. Taking action on living wages, particularly in the most affected industries and demographics, is crucial to achieving a more equitable and sustainable workforce.